
Principles of Ecology
*****************************************


FACTORS INFLUENCING DISTRIBUTION
Factors influencing the distribution of plant, animal species and population;
There are many factors that influence the distribution of plant, species and populations. These can affect both the size and density of a population.
Clouded leopards within the Southeast Asia, Unfortunately, their homelands have become harmful to their survival. This is because their environment has caused their population to suffer due to mankind has. These issues have caused a significant decrease in the clouded leopard population, leaving them to become on the endangered species list (Pataslides, 2009).
Some main ones may include;
-
Birth/death/morality rate
-
Age
-
Abiotic and biotic factors
-
Resources
-
Population fluctuations
-
Immigration/Emmigration
-
Climate Change (TutorVista, 2016).
-
Deforestation
-
Mining
-
Logging
-
Water
-
Age: The relative abundance of the organisms of various age groups in the population is called age distribution of population.
When relating to influences caused by age distribution, there are three kinds of populations involved, these are;
-
Rapidly growing: this population is which has high birth rate and low death rate, so there are more number of young individuals in the population.
-
Stationary population: this population, has equal birth and death rates, so population shows zero population growth.
-
Declining population: this population has higher death rate than birth rate, so the population has more numbers of older individuals.
Age Structure of the Hypothetical Populations are expected to increase, remain stable or decline with the passage of time (TutorVista, 2015).
Habitat destruction: An example of this would be that the clouded leopard’s natural environment is being harmed. This is because regions in which they redeem as their homes are decreasing due to logging companies removing trees from their natural habitat.
he development of numerous agricultural areas has also caused their habitat to diminish. It is becoming increasingly difficult for the leopards to find a sufficient place to survive in their distributed areas (Pataslides, 2009).
Climate Change: In the Borneo it is severely affected by climate change by the increasing risk of floods and forest fires, human health impacts, changes in agricultural yields and damages to infrastructure. Sea level rise is projected to cause widespread damage to population centers also.
This indicates that if the island of Borneo continues at its current rate of natural capital loss through deforestation, it will be severely affected by climate change (WWF, 2015).
“With two degrees of warming, Borneo’s rich biodiversity in marine, reptile and amphibian species will be severely affected, and potentially devastated by any warming beyond this level by 2050 as stated by (WWF, 2015)”.
Hunting: Rampant poaching, assisted by the increasing number of roads and logging trails, poses a grave threat to the Borneo’s endangered species i.e Clouded Leopard.
Wildlife crime is a big business which is run by dangerous international networks, wildlife and animal parts are trafficked like illegal drugs and arms. Experts at TRAFFIC the wildlife trade monitoring network, estimate that it continues to run into billions of dollars each year (WWF, 2015). Hunting has played a large role in the rapid decrease of the leopard population, this is due to them being hunted as game for their skins. These leopards are also hunted by commercial hunters that want the leopard’s skin, bones, and meat. They are sold to illegal wildlife traders, in which has an overall devastating effect on the clouded leopard population (Pataslides, 2009).
Mining: Borneo also holds rich metal and
mineral resources,
including tin, copper, gold, silver, coal,
diamonds, and different types of sand
and stone.
Together, the forestry and mining sectors
are the main contributors to forest loss
in Borneo (WWF, 2015).
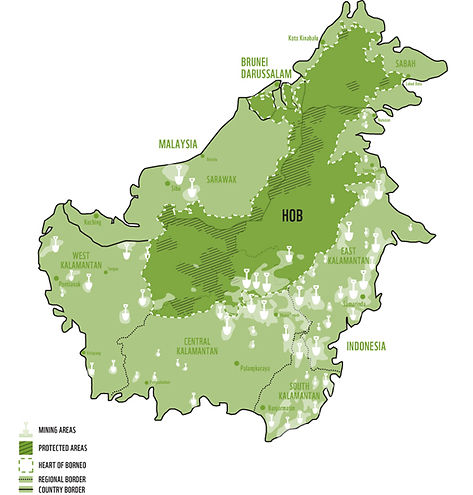
Mining influences on Borneo
(WWF, 2015).